2. Pathogen - Host Interaction
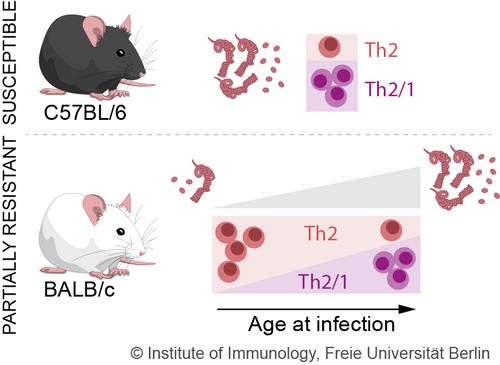
Fig. 1: Effects of ageing on the immune response against nematodes (Kapse et al. 2022)
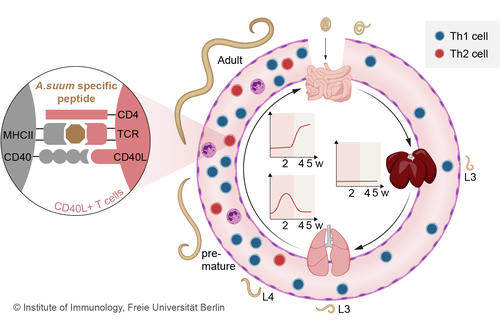
Fig. 2 T cell response during the course of an A. suum infection in the pig (Oser et al. 2024)
2.1 Th2/1 hybrid cells in nematode-infected patients and mice
In nematode infections, Th2/1 hybrid cells are induced, which we showed to stably express the transcription factors of the T helper type 1 and type 2 cells (Peine et al., 2013). Blood cells from patients infected with the threadworm Strongyloides stercoralis also showed significantly increased levels of not only GATA-3+ Th2 cells, but also GATA-3+T-bet+ cells. These Th2/1 hybrid cells are thus detectable in human infections, but express higher levels of IFN-g with very low GATA-3 expression compared to murine Th2/1 hybrids (Bock et al., 2017).
Interestingly, we also showed T cell numbers and their functions change with increasing age in response to a nematode infection. In older mice, compared to young mice, more T helper cells of type Th1 and T hybrid cells are detectable in response to the small intestinal nematode H. polygyrus (Fig. 1). In contrast, prominent T helper cell type Th2 response are found in young mice. This ageing phenomenon is associated with increased INF-g production in mice (Kapse et al., 2022).
Selected Publications
- Kapse, B.; Zhang, H.; Affinass, N.; Ebner, F.; Hartmann, S.; Rausch, S. (2022): Age-dependent rise in IFN-γ competence undermines effective type 2 responses to nematode infection. Mucosal Immunol; 15(6), S. 1270–1282
- Zhang, H.; Bednář, L.; Heitlinger, E.; Hartmann, S.; Rausch, S. (2022): Whip- and pinworm infections elicit contrasting effector and distinct regulatory responses in wild house mice. Int J Para; 52(8), S. 519–524
- Affinass, N.; Zhang, H.; Löhning, M.; Hartmann, S.; Rausch, S. (2018):Manipulation of the balance between Th2 and Th2/1 hybrid cells affects parasite nematode fitness in mice. Eur J Immunol; 48(12), S. 1958–1964
- Bock, C.N., S. Babu, M. Breloer, A. Rajamanickam, Y. Bhootra, M.-L. Brunn, A. A. Kühl, R. Merle, M. Löhning, S. Hartmann, S. Rausch (2017): Th2/1 hybrid cells occurring in murine and human strongyloidiasis share effector functions of Th1 cells, Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00261.
- Peine, M., S. Rausch, C. Helmstetter, A. Fröhlich, A. N. Hegazy, A. A. Kühl, C. G. Grevelding, T. Höfer, S. Hartmann, and M. Loehning (2013): Stable T-bet+GATA-3+ Th1/Th2 hybrid cells arise in vivo, can develop directly from naïve precursors, and limit immunopathologic inflammation. PLoS Biology, 11:e1001633.
Third-party funding: DFG GRK 2046: S. Rausch Project B5.
2.2 Regulation of antigen-presenting cells in nematode infections
Nematodes induce regulatory monocytes/macrophages, which are phagocytes and antigen-presenting cells. We demonstrated regulatory macrophages in mice treated with nematode antigen (Klotz et al., 2011) and in the blood of filarial-infected patients in South India (O'Regan et al., 2014). These regulatory macrophages influence independent inflammatory responses. Administration of nematode-induced regulatory macrophages in independent inflammatory events suppressed the inflammation and induced upregulation of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 by T helper cells (Ziegler et al., 2015). Thus, nematode-induced regulatory macrophages protect the host from nematode-induced pathology, but also from independent mucosal inflammation (Steinfelder et al., 2016).
Further, the intestinal porcine roundworm Ascaris suum utilized their secreted/excreted (ES) products to modulate the key antigen-presenting cell, the dendritic cell. Nematode ES induced a change in important dendritic cell surface markers and a suppression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine production IL-12 and TNF-a (Hamid et al., 2022).
Selected Publications
- Hamid, B.; Ebner, F.; Bechtold, L.; Kundik, A.; Rausch, S.; Hartmann, S. (2022):Ascaris suum excretory/secretory products differentially modulate porcine dendritic cell subsets.Front Immunol; 13, S. Artikel 1012717
- Hamid, B.; Schlosser-Brandenburg, J.; Bechtold, L.; Ebner, F.; Rausch, S.; Hartmann, S. (2021): Early immune initiation by porcine cells following Toxoplasma gondii infection versus TLR ligation. Microorganisms; 9(9), S. Artikel 1828
- Schlosser-Brandenburg, J.; Ebner, F.; Klopfleisch, R.; Kühl, A. A.; Zentek, J.; Pieper, R.; Hartmann, S. (2021): Influence of nutrition and maternal bonding on postnatal lung development in the newborn pig. Front Immunol; 12, S. Article 734153
- Strandmark, J.; Steinfelder, S.; Berek, C.; Kühl, A.; Rausch, S.; Hartmann, S. (2016): Eosinophils are required to suppress Th2 responses in Peyer’s patches during intestinal infection by nematodes. Mucosal Immunol; 10, S. 661–672
- Steinfelder, S., N.L. O’Regan, S. Hartmann (2016): Diplomatic Assistance: Can Helminth modulated macrophages act as treatment for inflammatory disease, PLoS Pathogens, DOI:10.1371
- Ziegler, T., S. Rausch, S. Steinfelder, C. Klotz, M.R. Hepworth, A. Kühl, P-C- Burda, R. Lucius, S. Hartmann (2015): A novel regulatory macrophage (Mreg) induced by a helminth molecule instructs IL-10 in CD4+ T-cells and protects against mucosal inflammation, J Immunology, 194:1555-1564.
Third-party funding: DFG GRK 2046: S. Hartmann Project B4.
2.3 Tools and T cell responses in pigs
In order to characterize T cell populations in pigs in response to infections, we have established the detection of lineage-specific T cell transcription factors and of antigen-specific T cells in pigs (Ebner et al., 2014, Schmidt et al., 2020). Using the marker CD154, pathogen-specific T cells can be analyzed during infection. A. suum-infected pigs showed a local, transient Th2 response in the lung and an accumulation of Th2 cells in the intestine after body migration of the larvae (Fig. 2), which was accompanied by a systemic Th1 expansion (Oser et al. 2024). The porcine model allows the characterization of pathogen-specific T cells of human-relevant infections and their distribution in the organs of the infected individual.
Selected Publications
- Oser, L., Midha, A., Schlosser-Brandenburg, J., Rausch, S., Mugo, R. M.; Kundik, A., Elizalde-Velázquez, L. E., Adjah, J., Musimbi, Z. D., Klopfleisch, R.; Helm, C. S., von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G., Hartmann, S., Ebner, F. (2024): Ascaris suum infection in juvenile pigs elicits a local Th2 response in a setting of ongoing Th1 expansion, Front Immunol; doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1396446
- Schlosser-Brandenburg, J.; Ebner, F.; Klopfleisch, R.; Kühl, A. A.; Zentek, J.; Pieper, R.; Hartmann, S. (2021): Influence of nutrition and maternal bonding on postnatal lung development in the newborn pig. Front Immunol; 12, S. Article 734153
- Schmidt, S.; Ebner, F.; Rosen, K.; Kniemeyer, O.; Brakhage, A. A.; Löffler, J.; Seif, M.; Springer, J.; Schlosser, J.; Scharek-Tedin, L.; Scheffold, A.; Bacher, P.; Kühl, A. A.; Rösler, U.; Hartmann, S. (2020):The domestic pig as human‐relevant large animal model to study adaptive anti‐fungal immune responses against airborne Aspergillus fumigatus. Eur J Immunol; 50(11), S. 1712–1728
- Ebner, F.; Morrison, E.; Bertazzon, M.; Midha, A.; Hartmann, S.; Freund, C.; Álvaro-Benito, M. (2020): CD4+ Th immunogenicity of the Ascaris spp. secreted products. Vaccine; 5, S. Article number: 25
- Ebner, F., P. Schwiertz, S. Steinfelder, R. Pieper, J. Zentek, N. Schütze, C. G. Baums, G. Alber, P. Geldhof, S. Hartmann. 2017. Pathogen-reactive T helper cell analysis in the pig, Frontiers in Immunology, doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00565.
Third-party funding: DFG GRK 2046: F. Ebner Project C9.
2.4 Parasite - Host Interaction
In the frame of the priority program Physis of Parasitism (POP, DFG SPP 2332), this joint project with Anja Hauser (DRFZ/Charité Berlin) investigates the interactions of the natural rodent parasite Giarida muris with the murine host. Giardia trophozoites are excellent swimmers equipped with four pairs of flagella, but the parasite primarily resists expulsion from the host gut by firm adhesion to the epithelial cells using a ventral adhesive disc. Combining in vitro work with intravital imaging, we investigate Giardia locomotion depending on microenvironment parameters and determine the adhesion forces exerted by the parasite during adhesion to non-biological surfaces and host epithelial cells. A further focus is on the impact of G. muris attachment forces on host cells in vivo. We thereby aim to define the physical parameters of Giardia-host cell interactions in the genuine host environment, using a naturally adapted parasite which causes minimal pathology and reflects the asymptomatic course seen in many humans infected with G. duodenalis.
Selected Publications
- Yordanova, I.A., Cortés, A., Klotz, C., Kühl, A.A., Heimesaat, M.M., Cantacessi, C., Hartmann, S., Rausch, S., 2019.
RORγt+ Treg to Th17 ratios correlate with susceptibility to Giardia infection. Sci. Rep. 9, 20328.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56416-9 - Yordanova, I.A., Lamatsch, M., Kühl, A.A., Hartmann, S., Rausch, S., 2021. Eosinophils are dispensable for the
regulation of IgA and Th17 responses in Giardia muris infection. Parasite Immunol. 43, e12791.
doi: 10.1111/pim.12791
Third-party funding: DFG SPP 2332 (Physics of Parasitism): Anja Hauser and S. Rausch Project P13.