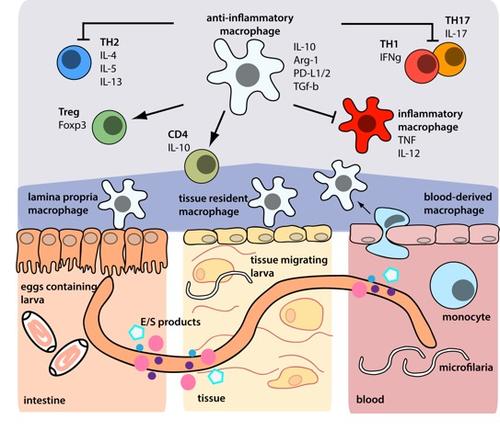
Regulatory macrophages in nematode infections
Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of nematode-modulated macrophages/monocytes in the intestine, skin and blood (Steinfelder et al. PLOS Pathogens, 2016).
Image Credit: Institut für Immunologie
Nematodes induce regulatory monocytes/macrophages as shown by us in mice (Klotz et al. PLOS Pathogens, 2011) and, in cooperation with Dr. A. Srikantam (Blue Peter Research Center, Hyderabad, India), in blood of filariasis patients in South India (O’Regan et al. PLOS NTD, 2014). In addition, nematode-induced regulatory macrophages modulate unrelated inflammatory reactions. Adoptive transfers of nematode-induced regulatory macrophages in a mouse model of allergic hyperreactivity suppress various parameters of allergic reactions and lead to the local and systemic induction of IL-10 in CD4+ T cells (Ziegler et al. Journal of Immunology, 2015). Thus, nematode-induced regulatory macrophages protect the host against infection-driven pathological processes, but also from unrelated inflammatory immune reactions (figure, Steinfelder et al. PLOS Pathogens, 2016).
Selected publications:
- Klotz, C., T. Ziegler, A.S. Figueiredo, S. Rausch, M. Hepworth, C. Sers, R. Lang, P. Hammerstein, R. Lucius, S. Hartmann. 2011. A helminth immunomodulator exploits host signaling events to regulate cytokine production in macrophages. PLoS Pathogens, 7:e1001248.
- O’Regan, N.L, S. Steinfelder, G. Venugopal, G.B. Rao, R. Lucius, A. Srikantam, S. Hartmann. 2014. Brugia malayi microfilariae induce a regulatory monocyte/macrophage phenotype that suppresses innate and adaptive immune responses. PLoS NTD, 8:e3206.doi:10.1371.
- Ziegler, T., S. Rausch, S. Steinfelder, C. Klotz, M.R. Hepworth, A. Kühl, P-C- Burda, R. Lucius, S. Hartmann. 2015. A novel regulatory macrophage (Mreg) induced by a helminth molecule instructs IL-10 in CD4+ T-cells and protects against mucosal inflammation, J. Immunology, 194:1555-1564.
- Steinfelder, S., N.L. O’Regan, S. Hartmann. 2016. Diplomatic Assistance: Can Helminth modulated macrophages act as treatment for inflammatory disease, PLoS Pathogens, DOI:10.1371
Associated scientists: Dr. Svenja Steinfelder, Gopinath Venugopal.